栈和队列(顺序表、单链表形式)
栈和队列
- 栈
- 栈.顺序表
- 结构体的设计
- 栈的初始化
- 栈的销毁
- 入栈
- 出栈
- 获取栈顶数据
- 判断栈空
- 栈中有效元素的个数
- Stack.h
- Stack.c
- test.c
- 栈.单链表
- 结构体设计
- 栈的初始化
- 栈的销毁
- 入栈
- 出栈
- 获取栈顶元素
- 判断栈是否为空
- 获取栈中元素个数
- Stack.h
- Stack.c
- test.c
- 队列
- 队列.顺序表
- 结构体的设计
- 队列的初始化
- 队列的销毁
- 入队
- 出队
- 获取队头
- 获取队尾元素
- 获取队列有效元素
- 判断队列是否为空
- Queue.h
- Queue.c
- test.c
- 队列.单列表
- 结构体设计
- 初始化
- 链表的销毁
- 入队
- 出队
- 获取队头元素
- 获取队尾元素
- 获取队列元素个数
- 判断队列是否为空
- Queue.h
- Queue.c
- test.c
- 结束语
栈
栈的主要特点:后进先出
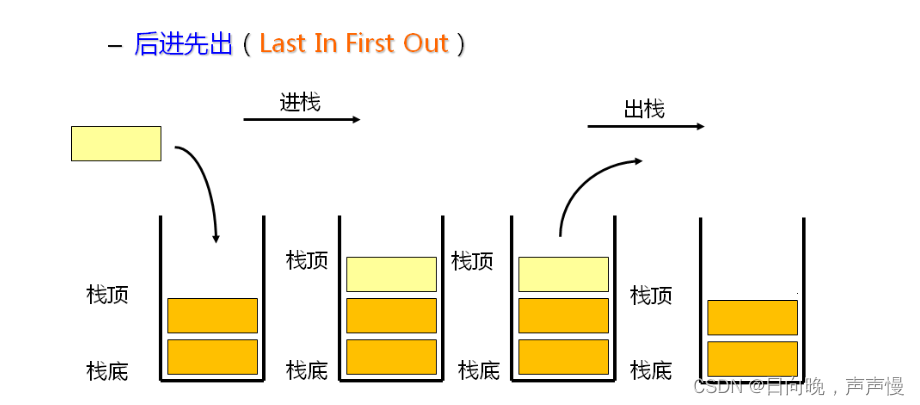
栈顶是动态的,栈底是静态的。即只能从栈顶进,从栈顶出。
还是看不懂,可以想一下弹夹
找了半天只看到这个,后进去的子弹先出来

栈的存储结构可以是顺序表,也可以是单链表。
不管栈还是队列,操作方面都是基于顺序表和单链表,换而言之,这两个存储结构的基本操作,你必须掌握。操作并不是这一篇博客的重点,重点是思路和分析易错的地方
栈.顺序表
如果选取顺序表,顺序表的优点是尾插,尾删的时间复杂度O(1),所以说栈顶是在尾部。这里是高级货色,是动态版本的顺序表改版,换句话说,你需要对动态内存管理的函数要有了解,特别是
realloc。上过热榜的C动态管理
结构体的设计
将元素类型重命名好处:当元素是其他类型时候,只要改动一行代码就可以了。
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int sz;int top;//栈顶
}Stack;
内存布局
栈的初始化
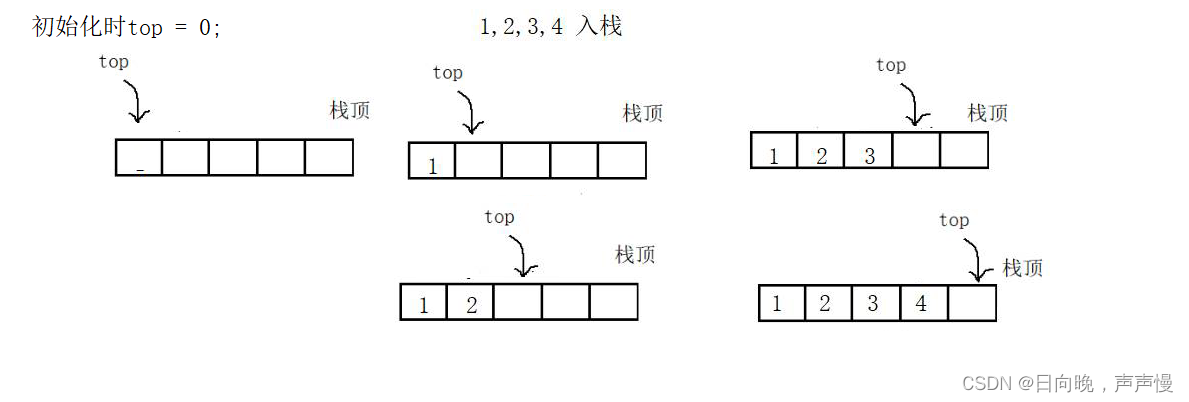
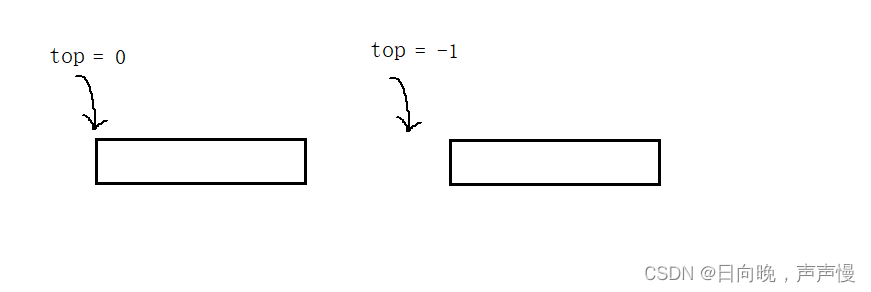
这里存在两种设计,栈顶
top的初始值是-1还是0。当top ==-1时,top表示栈顶元素,当top == 0时,top表示栈顶下一个元素,这里采用的top == 0。
刚开始
a = NULL,是通过下面入栈操作去开辟空间,你也可以直接先申请空间,再去扩容
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{pst->a = NULL;pst->top = 0;//指向栈顶元素的下一个pst->sz = 0;
}
栈的销毁
将堆区的空间释放并且置为
NULL
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->sz = 0;pst->top = 0;
}
入栈
C动态内存管理
三个注意事项:
①:realloc:当传入NULL功能和malloc一样。
②:realloc:开辟空间的大小 = 扩容大小+原来空间大小
③:memset:来初始化,要注意起始位置。
assert的作用:如果pst是空指针就报错。
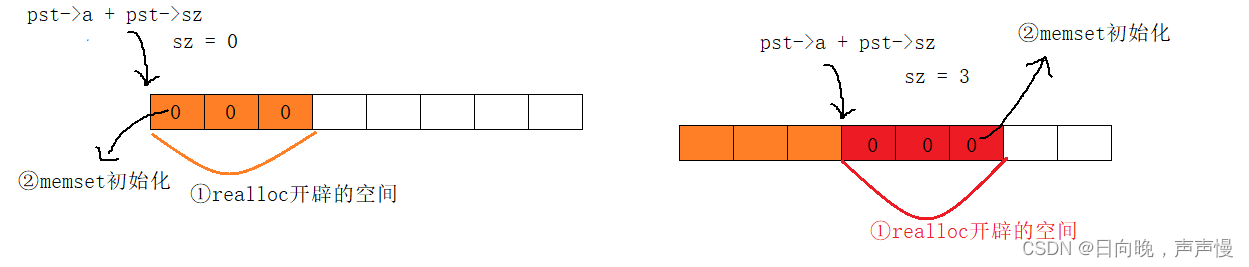
//添加空间
void AddSpace(Stack* pst)
{STDataType* p = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, \sizeof(STDataType) * (pst->sz + 3));if (NULL == p){perror("AddSpace::\n");}memset(p + pst->sz, 0, sizeof(STDataType) * 3);pst->a = p;pst->sz += 3;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top >= pst->sz){AddSpace(pst);}pst->a[pst->top] = x;//top是栈顶元素的下一个pst->top++;
}
出栈
除了
assert(pst);还要考虑当栈空的时候,还能出栈吗?肯定是不能,所以assert(pst->top > 0);暴力检测。
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}
获取栈顶数据
注意
top是栈顶的下一个元素,所以需要-1。
STDataType TopPop(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
判断栈空
bool类型是用来判断真假的,只存在两个值true和false,true == 1表示真,false == 0表示假。栈非空为真,栈空为假。
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);return !(0 == pst->top);
}
栈中有效元素的个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int sz;int top;//栈顶
}Stack;//对栈初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
//销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);
//压栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x);
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
//弹出栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
//判断栈空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst);
//计算栈中的元素
int StackSize(Stack* pst);
Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"
//栈的初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{pst->a = NULL;pst->top = 0;//指向栈顶元素的下一个pst->sz = 0;
}
//栈的销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->sz = 0;pst->top = 0;
}
//添加空间
void AddSpace(Stack* pst)
{STDataType* p = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, \sizeof(STDataType) * (pst->sz + 3));if (NULL == p){perror("AddSpace::\n");}memset(p + pst->sz, 0, sizeof(STDataType) * 3);pst->a = p;pst->sz += 3;
}
//压栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top >= pst->sz){AddSpace(pst);}pst->a[pst->top] = x;//top是栈顶元素的下一个pst->top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}
//获取栈顶数据
STDataType TopPop(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//判断栈空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);return !(0 == pst->top);
}
//栈中的大小
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
test.c
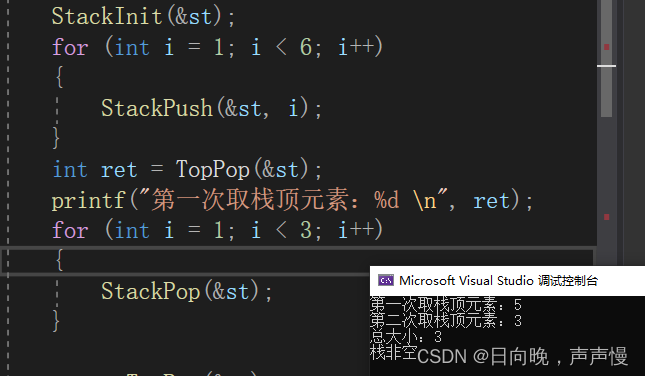
#include"Stack.h"int main()
{Stack st;StackInit(&st);for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++){StackPush(&st, i);}int ret = TopPop(&st);printf("第一次取栈顶元素:%d \n", ret);for (int i = 1; i < 3; i++){StackPop(&st);}ret = TopPop(&st);printf("第二次取栈顶元素:%d \n", ret);int sz = StackSize(&st);printf("总大小:%d\n", sz);if (StackEmpty(&st))printf("栈非空\n");elseprintf("栈空\n");StackDestroy(&st);return 0;
}
栈.单链表
单链表适合头插,头插的时间复杂度为O(1),换句话说,栈顶应该指向链表第一个节点,把栈顶当作头指针使用即可。
结构体设计
这样设计以后,一个好处:上面顺序表是对应,意思和顺序表的
Stack.c和Stack.h更换,主函数不变,运行结果还是一样的效果。另一个好处,结构分明。
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct StNode
{STDataType data;struct StNode* next;
}StNode;
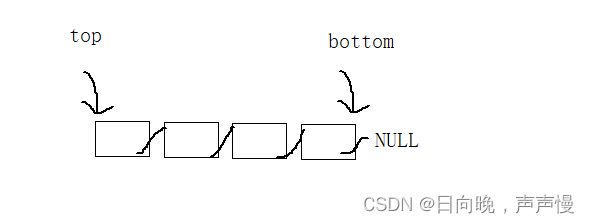
typedef struct Stack
{StNode* top;//栈顶StNode* bottom;
}Stack;
栈的初始化
void StackInit(Stack* st)
{assert(st);st->top = NULL;st->bottom = NULL;
}
栈的销毁
销毁完成后,指针需要置为
NULL
void StackDestroy(Stack* st)
{assert(st);StNode* p = st->top;while (p){StNode* tmp = p;p = p->next;free(tmp);}st->bottom = NULL;st->top = NULL;
}
入栈
将开辟节点和初始化节点,封装成函数,看起来更舒服一点,用起来也很方便。
这里是没有哨兵位头节点,当一开始指针指向NULL的时候要特殊处理。
//开辟节点
StNode* AollocStNode(STDataType x)
{StNode* newnode = (StNode*)malloc(sizeof(StNode));newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;return newnode;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* st, STDataType x)
{assert(st);StNode* newnode = AollocStNode(x);if (st->bottom == NULL)st->bottom = newnode;//头插if (st->top == NULL)st->top = newnode;else{newnode->next = st->top;st->top = newnode;}
}
出栈
出栈操作就是释放第一个节点,然后让
top指向下一个节点
当最后一个节点也出栈了,别忘记bottom也要置为NULL。
栈空的时候,也不能出栈,因此assert(st->top)暴力检测一下。
void StackPop(Stack* st)
{assert(st);assert(st->top);StNode* p = st->top;st->top = p->next;free(p);if (st->top == NULL)st->bottom = NULL;
}
获取栈顶元素
栈空了不能获取,因此也要
assert检查一下。
STDataType TopPop(Stack* st)
{assert(st);assert(st->top);return st->top->data;
}
判断栈是否为空
栈空返回
false,栈非空返回true
bool StackEmpty(Stack* st)
{assert(st);return !(st->top == NULL);
}
获取栈中元素个数
可别直接拿
top去循环,不然top指向会改变,找不到原来的第一个节点了,需要一个中间变量。
int StackSize(Stack* st)
{assert(st);int count = 0;StNode* p = st->top;while (p){count++;p = p->next;}return count;
}
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#includetypedef int STDataType;
typedef struct StNode
{STDataType data;struct StNode* next;
}StNode;
typedef struct Stack
{StNode* top;//栈顶StNode* bottom;
}Stack;//初始化
void StackInit(Stack* st);
//销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* st);
//压栈
void StackPush(Stack* st,STDataType x);
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* st);
//弹出栈顶元素
STDataType TopPop(Stack* st);
//判断栈空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* st);
//判断栈中有效元素
int StackSize(Stack* st);
Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"
//初始化
void StackInit(Stack* st)
{assert(st);st->top = NULL;st->bottom = NULL;
}
//销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* st)
{assert(st);StNode* p = st->top;while (p){StNode* tmp = p;p = p->next;free(tmp);}st->bottom = NULL;st->top = NULL;
}
//开辟节点
StNode* AollocStNode(STDataType x)
{StNode* newnode = (StNode*)malloc(sizeof(StNode));newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;return newnode;
}
//压栈
void StackPush(Stack* st, STDataType x)
{assert(st);StNode* newnode = AollocStNode(x);if (st->bottom == NULL)st->bottom = newnode;if (st->top == NULL)st->top = newnode;else{newnode->next = st->top;st->top = newnode;}
}//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* st)
{assert(st);assert(st->top);StNode* p = st->top;st->top = p->next;free(p);if (st->top == NULL)st->bottom = NULL;
}
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType TopPop(Stack* st)
{assert(st);assert(st->top);return st->top->data;
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* st)
{assert(st);return !(st->top == NULL);
}
//返回有效的元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* st)
{assert(st);int count = 0;StNode* p = st->top;while (p){count++;p = p->next;}return count;
}
test.c
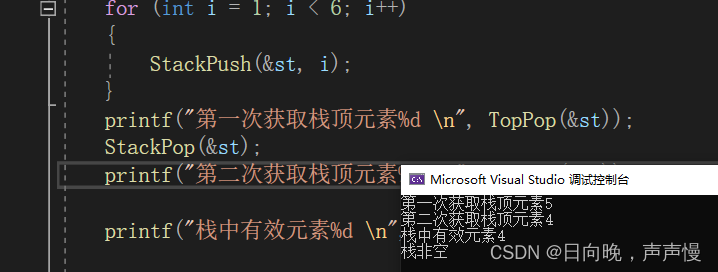
#include"Stack.h"int main()
{Stack st;StackInit(&st);for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++){StackPush(&st, i);}printf("第一次获取栈顶元素%d \n", TopPop(&st));StackPop(&st);printf("第二次获取栈顶元素%d \n", TopPop(&st));printf("栈中有效元素%d \n", StackSize(&st));if (StackEmpty(&st))printf("栈非空\n");elseprintf("栈空\n");StackDestroy(&st);return 0;
}
队列
队列的主要特点:先进先出。
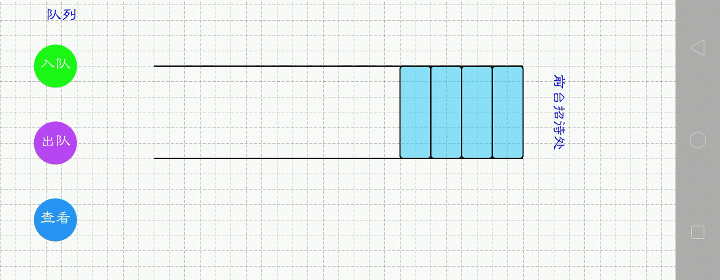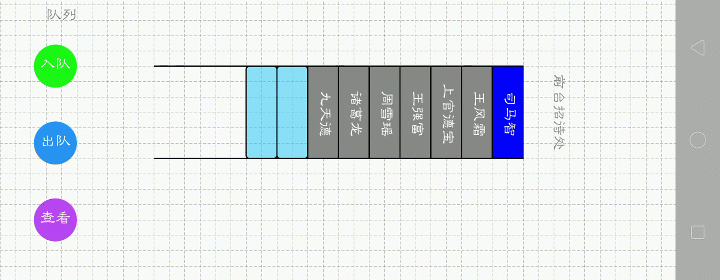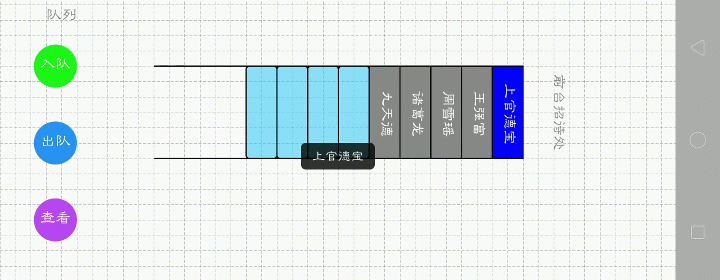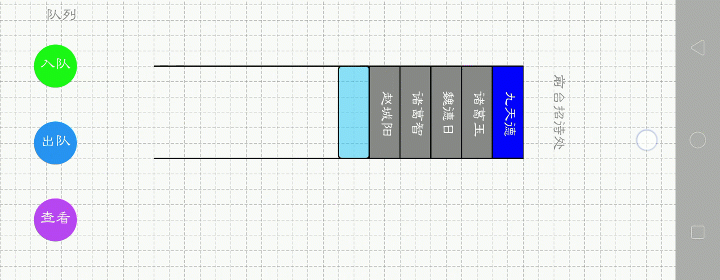
队列.顺序表
下面哪一种更好呢?第一种。比如1,2,3,4要入队,第一种看起来更直接,操作也方便,只要尾插就行。而第二种,需要前插时间复杂度就大了。我用的是第一种。
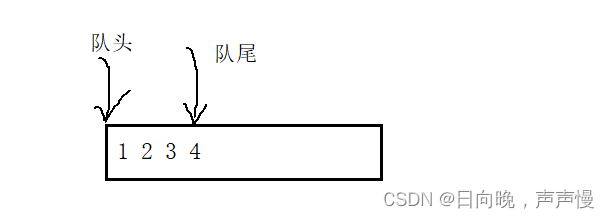
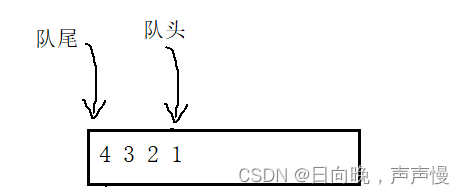
结构体的设计
这就和栈那里的设计相差无几了.
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct Queue
{QDataType* a;int capacity;int rear;//队尾//队头下标为0处
}Queue;
队列的初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{q->a = NULL;q->capacity = 0;q->rear = 0;//也存在两种初始化-1和0//0:队尾的下一个元素
}
队列的销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{assert(q);free(q->a);q->a = NULL;q->capacity = 0;q->rear = 0;
}
入队
单个
\是续行符,同样是三个注意事项,不再赘述。
void AddSpace(Queue* q)
{QDataType* p = (QDataType*)realloc(q->a, \sizeof(QDataType) * (3 + q->capacity));if (NULL == p)perror("AddSpace::\n");memset(p + q->capacity, 0, sizeof(QDataType) * 3);q->a = p;q->capacity += 3;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x)
{assert(q);if (q->rear >= q->capacity)AddSpace(q);q->a[q->rear] = x;q->rear++;
}出队
队列为空的时候不能出队,因此加上
assert(q->rear > 0)检测
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear > 0);for (int i = 0; i < q->rear-1; i++){q->a[i] = q->a[i + 1];}q->rear--;
}
获取队头
队列为空时,不可获取
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear > 0);return q->a[0];
}
获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear > 0);return q->a[q->rear - 1];
}
获取队列有效元素
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{assert(q);return q->rear;
}
判断队列是否为空
队列为空返回
false,队列非空返回true
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{assert(q);return !(0 == q->rear);
}
Queue.h
#include
#include
#include
#include
#includetypedef int QDataType;typedef struct Queue
{QDataType* a;int capacity;int rear;//队尾//队头下标为0处
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x);
//出队
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
//获取队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
//获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
//判断队空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
//获取队列有效元素
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{q->a = NULL;q->capacity = 0;q->rear = 0;//也存在两种初始化-1和0//队尾的下一个元素
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{assert(q);free(q->a);q->a = NULL;q->capacity = 0;q->rear = 0;
}
//入队
void AddSpace(Queue* q)
{QDataType* p = (QDataType*)realloc(q->a, \sizeof(QDataType) * (3 + q->capacity));if (NULL == p)perror("AddSpace::\n");memset(p + q->capacity, 0, sizeof(QDataType) * 3);q->a = p;q->capacity += 3;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x)
{assert(q);if (q->rear >= q->capacity)AddSpace(q);q->a[q->rear] = x;q->rear++;
}//出队
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear > 0);for (int i = 0; i < q->rear-1; i++){q->a[i] = q->a[i + 1];}q->rear--;
}
//获取队头
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear > 0);return q->a[0];
}
//获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear > 0);return q->a[q->rear - 1];
}
//获取队列有效元素
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{assert(q);return q->rear;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{assert(q);return !(0 == q->rear);
}test.c
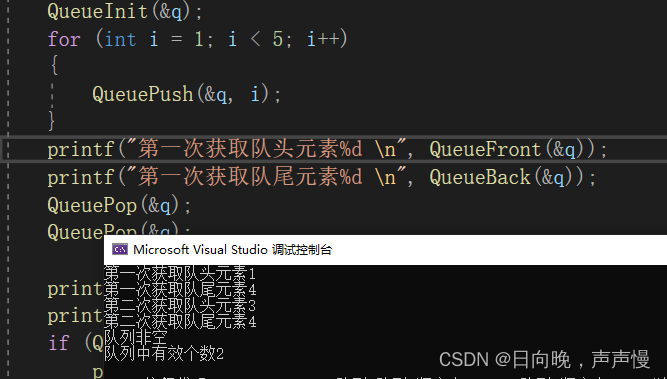
#include"Queue.h"int main()
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++){QueuePush(&q, i);}printf("第一次获取队头元素%d \n", QueueFront(&q));printf("第一次获取队尾元素%d \n", QueueBack(&q));QueuePop(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("第二次获取队头元素%d \n", QueueFront(&q));printf("第二次获取队尾元素%d \n", QueueBack(&q));if (QueueEmpty(&q))printf("队列非空\n");elseprintf("队列空\n");printf("队列中有效个数%d \n", QueueSize(&q));QueueDestroy(&q);return 0;
}
队列.单列表
队列用单链表去写才是最好的,设计巧妙的话,入队和出队时间复杂度可以O(1)。
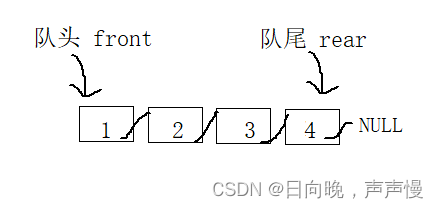
用带哨兵位头节点的双向循环链表,出队和入队的时间复杂度是O(1),可以尝试写一写
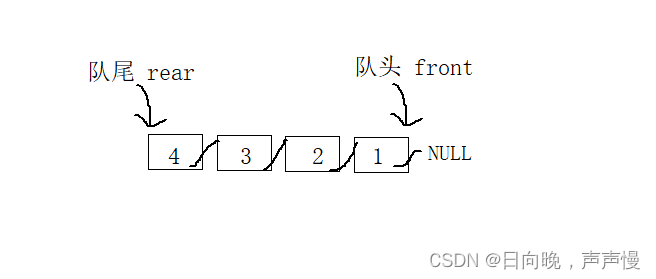
下面这种形式,入队和出队能时间复杂度为O(1),入队:通过rear进行尾插,因为rear指向链表尾部。出队:用front进行头删。
1,2,3,4入队

下面这种,入队只能头插O(1),出队尾删O(n)。1,2,3,4入队
结构体设计
和
Stack设计是差不多的
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QListNode
{QDataType data;struct QListNode* next;}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* front;QNode* rear;
}Queue;
初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{assert(q);q->front = NULL;//队头是链表的头q->rear = NULL;//队尾是链表的尾
}
链表的销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{assert(q);QNode* p = q->front;while (p){QNode* tmp = p;p = p->next;free(tmp);}q->front = NULL;q->rear = NULL;
}
入队
入队是尾插。需要注意,第一次入队的时候,两个指针都是
NULL,需要特殊处理一下。
//开辟节点
QNode* AollocQNode(QDataType x)
{QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x)
{assert(q);QNode* newnode = AollocQNode(x);if (NULL == q->front)q->front = newnode;if (NULL == q->rear)q->rear = newnode;else{q->rear->next = newnode;q->rear = newnode;}
}
出队
头删操作,当删除最后一个节点的时候,不能忘记
rear也要置为NULL
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->front);QNode* p = q->front;//头指针q->front = q->front->next;free(p);if (q->front == NULL)q->rear = NULL;
}
获取队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->front);return q->front->data;
}
获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear);return q->rear->data;
}
获取队列元素个数
需要中间变量,去遍历队列,不能改变
front的指向
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{assert(q);QNode* p = q->front;int count = 0;while (p){p = p->next;count++;}return count;
}
判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{assert(q);return !(q->rear == NULL);
}
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#includetypedef int QDataType;
// 链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QListNode
{QDataType data;struct QListNode* next;}QNode;// 队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* front;QNode* rear;
}Queue;//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x);
//出队
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
//获取队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
//获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
//获取队列中有效元素
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q); Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{assert(q);q->front = NULL;//队头是链表的尾q->rear = NULL;//队尾是链表的头
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{assert(q);QNode* p = q->front;while (p){QNode* tmp = p;p = p->next;free(tmp);}q->front = NULL;q->rear = NULL;
}
//开辟节点
QNode* AollocQNode(QDataType x)
{QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x)
{assert(q);QNode* newnode = AollocQNode(x);if (NULL == q->front)q->front = newnode;if (NULL == q->rear)q->rear = newnode;else{q->rear->next = newnode;q->rear = newnode;}
}
//出队
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->front);QNode* p = q->front;//头指针q->front = q->front->next;free(p);if (q->front == NULL)q->rear = NULL;
}//获取队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->front);return q->front->data;
}
//获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{assert(q);assert(q->rear);return q->rear->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{assert(q);QNode* p = q->front;int count = 0;while (p){p = p->next;count++;}return count;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{assert(q);return !(q->rear == NULL);
}
test.c
#include"Queue.h"int main()
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++){QueuePush(&q, i);}int ret = QueueFront(&q);printf("第一次取队头元素:%d\n", ret);ret = QueueBack(&q);printf("第一次取队尾元素:%d\n", ret);QueuePop(&q);ret = QueueFront(&q);printf("第二次取队头元素:%d\n", ret);ret = QueueBack(&q);printf("第二次取队尾元素:%d\n", ret);ret = QueueSize(&q);printf("队列中有效元素:%d \n", ret);if (QueueEmpty(&q))printf("队列非空\n");elseprintf("队列空\n");//for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++)//{// QueuePop(&q);//}if (QueueEmpty(&q))printf("队列非空\n");elseprintf("队列空\n");QueueDestroy(&q);return 0;
}
结束语
还等什么,还不打开vs,埋头苦干起来,要是没看的太明白,建议先熟练顺序表和单链表的基本操作。