linux 进程通信 C程序案例
创始人
2024-01-21 04:12:20
0次
linux 进程通信 C程序案例
编写C程序完成:父进程创建两个子进程,每个进程都在屏幕上显示自己的进程ID号,并在第1个子进程中加载执行一条外部命令。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{pid_t c1 = fork();if(c1 == 0) //child1{ printf("[%d] : child1\n", getpid());execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", "date", (char *)0);}else if(c1 > 0) //parent{ printf("[%d] : parent\n", getpid());pid_t c2 = fork();if(c2 == 0) //child2{printf("[%d] : child2\n", getpid());}else if(c2 > 0) //parent{ printf("[%d] : parent\n", getpid());int status;wait(&status);}}return 0;
}
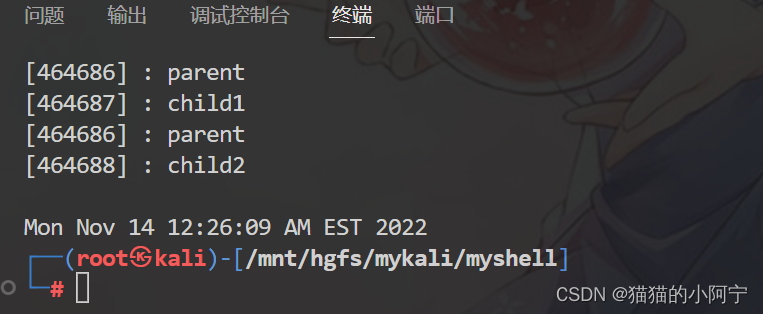
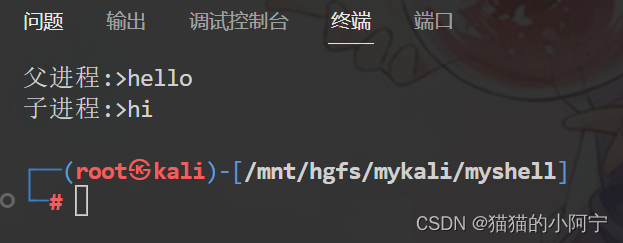
编写C程序完成:父进程创建1个子进程,然后建立无名管道与子进程互相传递问候信息(父进程发出“hello!”,子进程发出“Hi!”),最后各自将接收到的信息输出到屏幕。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include int main()
{char *parent_talk[] = {"hello", NULL};char *child_talk[] = {"hi", NULL};int fd1[2];int fd2[2];int res = pipe(fd1);if (res == -1){printf("create pipe error.\n");exit(1);}res = pipe(fd2);if (res == -1){printf("create pipe erroe.\n");exit(1);}pid_t pid;pid = fork();if (pid == 0) //子进程{close(fd1[1]); //子进程关闭fd1的写端,关闭fd2的读端close(fd2[0]);char buf[256];int i;char *talk = child_talk[i];while (talk != NULL){sleep(5);read(fd1[0], buf, 256);printf("父进程:>%s\n", buf);write(fd2[1], talk, strlen(talk) + 1);i++;talk = child_talk[i];}close(fd1[0]);close(fd2[1]);}else if (pid > 0){close(fd1[0]); //父进程关闭fd1的读端,关闭fd2的读端close(fd2[1]);char buf[256];int i = 0;char *talk = parent_talk[i];while (talk != NULL){write(fd1[1], talk, strlen(talk) + 1);read(fd2[0], buf, 256);printf("子进程:>%s\n", buf);i++;talk = parent_talk[i];}close(fd1[1]);close(fd2[0]);int status;wait(&status);}return 0;
}
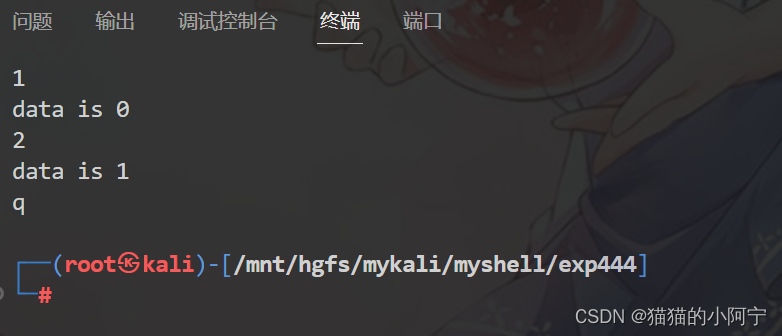
理解创建进程的系统调用并分析fork()与vfork()异同。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(void)
{int data = 0;pid_t pid;int choose = 0;while ((choose = getchar()) != 'q'){switch (choose){case '1':pid = fork();// fork的返回值,大于0 的时候,代表是父进程。此时的返回值,刚好是子进程的pid号// fork的返回值,等于0 的时候,代表的是子进程。此时的子进程的pid号其实是复制了fork大于0 的返回值。if (pid < 0)printf("Error !\n");if (pid == 0) // 子进程执行后+1{data++;exit(0);}wait(NULL);if (pid > 0)printf("data is %d\n", data); // 子进程未执行 ,为 0break;case '2':pid = vfork(); // vfork():保证子进程先运行if (pid < 0) // 出错perror("Error !\n");if (pid == 0) // 子进程执行后+1{data++;exit(0);}wait(NULL);if (pid > 0)printf("data is %d\n", data); // 由于vfork保证子进程先运行 所以为1break;default:break;}}return 0;
}
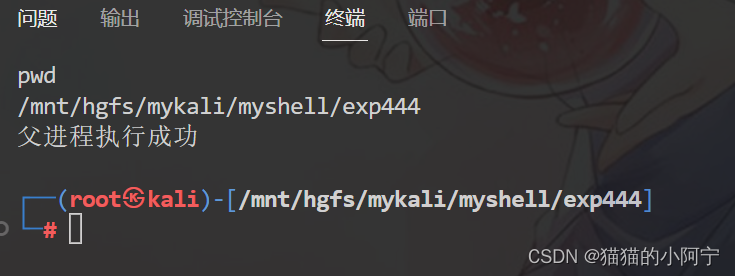
实现一个程序启动另一个程序后自身仍然在运行,即在子进程中加载执行其他程序而父进程等待子进程结束后才结束。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{/*接受键盘输入命令字符*/char buf[88];fgets(buf, 88, stdin);pid_t pid;pid = fork();/*创建子进程*/if (pid < 0)perror("创建子进程失败");else if (0 == pid){/*用exec()加载程序执行输入的命令*/execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", buf, (char *)0);}else{/*等待子进程信息*/wait(NULL);/*继续父进程的执行*/printf("父进程执行成功");}
}
编写一段C语言程序使其完成:父子进程通过无名管道传递三条消息:
- 管道文件的测试程序开始
- 管道文件测试正在进行
- 管道通信测试结束
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/*进程间通信(IPC机制)通信方式有: 管道 有名管道 消息队列 信号量 共享内存 套接字管道:是一种半双工的通信方式 只能在具有亲缘关系的进程间使用有名管道:也是半双工的通信方式,但是它允许无亲缘关系进程间的通信
*///实现父子进程之间相互发送消息
int main()
{char *parent_talk[] = {"管道文件的测试程序开始", "管道文件测试正在进行", "管道通信测试结束", NULL};char *child_talk[] = {"好的", "一切正常", "拜拜", NULL};int fd1[2];int fd2[2];int res = pipe(fd1);if (res == -1){printf("create pipe error.\n");exit(1);}res = pipe(fd2);if (res == -1){printf("create pipe erroe.\n");exit(1);}pid_t pid;pid = fork();if (pid == 0) //子进程{close(fd1[1]); //子进程关闭fd1的写端,关闭fd2的读端close(fd2[0]);char buf[256];int i;char *talk = child_talk[i];while (talk != NULL){sleep(5);read(fd1[0], buf, 256);printf("父进程:>%s\n", buf);write(fd2[1], talk, strlen(talk) + 1);i++;talk = child_talk[i];}close(fd1[0]);close(fd2[1]);}else if (pid > 0){close(fd1[0]); //父进程关闭fd1的读端,关闭fd2的读端close(fd2[1]);char buf[256];int i = 0;char *talk = parent_talk[i];while (talk != NULL){write(fd1[1], talk, strlen(talk) + 1);read(fd2[0], buf, 256);printf("子进程:>%s\n", buf);i++;talk = parent_talk[i];}close(fd1[1]);close(fd2[0]);int status;wait(&status);}return 0;
}

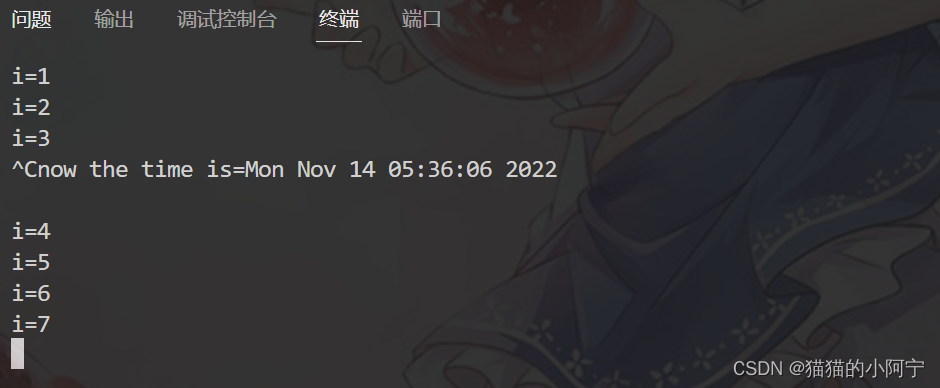
利用Linux/UNIX的软中断信号,编写一段C语言程序完成:显示数字1到100,在程序运行中如果捕获到一个SIGINT信号,则转去执行一段显示当前系统时间的程序。在编程中要考虑到信号被复位的情况,使程序能够实现多次被打断却多次的恢复执行。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void handler(int signo)
{signal(SIGINT, SIG_IGN);time_t timep;time(&timep);printf("now the time is=%s\n", asctime(gmtime(&timep)));signal(SIGINT, handler);
}
int main()
{int i;signal(SIGINT, handler);for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++){printf("i=%d\n", i);sleep(1);}printf("the program ends!\n");return 0;
}
编写一段C程序完成:父进程创建一个子进程,父进程对子进程设置一个报警信号,然后父进程等待子进程的结束,如果此时报警信号先到,就终止子进程。在程序中尽量返回子进程的退出码。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include // https://blog.csdn.net/awawfwfw/article/details/46519251void killchild(int pid_child);void killchild(int pid_child)
{printf("killing child process \n");//调用wait函数int pidxx;pidxx = wait(NULL);printf("killed the child process, whose pid is %d \n", pidxx);exit(0);
}void killyourself(int ownid);
void killyourself(int ownid)
{// printf("killing child process %d \n",pid_child);printf("parent sent signal, child process killed itself \n");exit(0);
}int main()
{// 要捕捉的信号(void)signal(SIGALRM, killchild);int pid_child = 0;int pid = fork();if (pid == -1){perror("fork failed\n");// exit(1);exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}if (pid == 0){//子进程pid_child = getpid();//子进程也signal一个信号(void)signal(SIGHUP, killyourself);sleep(15);kill(getppid(), SIGALRM);}else{//父进程//等待// pause();sleep(6);kill(pid_child, SIGHUP);exit(0);}
}
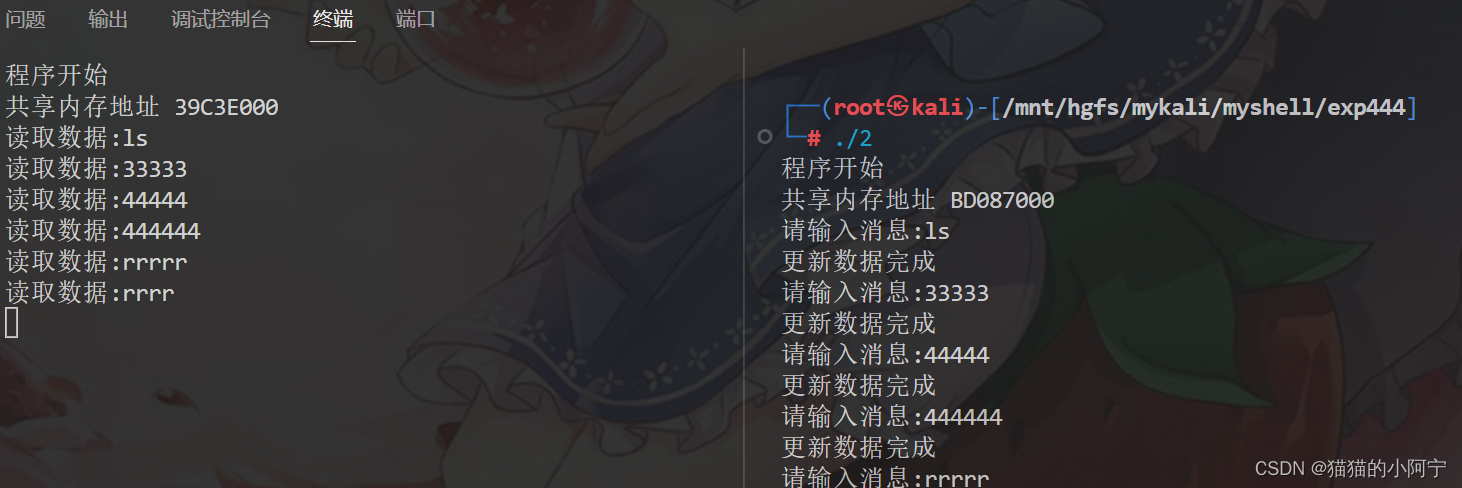
编写一个C语言程序使其完成:两个程序testl和test2通过一个共享内存进行通信,其中testl向共享内存中写数据,test2从共享内存中读出数据或信息并将数据或信息送入标准输出上。
test1
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include struct shared_msg
{int update; //更新数据标志,1:更新,0:未更新char text[BUFSIZ]; //记录写入和读取的文本
};
void main()
{printf("程序开始\n");key_t key; //共享内存键值int shmid; //共享内存标识char buf[BUFSIZ]; //输入缓冲struct shared_msg *msg; //共享内存地址//得到键值key = (key_t)1234;//创建共享内存shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct shared_msg), IPC_CREAT | 0666);if (shmid < 0){//输出到错误缓冲区fprintf(stderr, "创建共享内存失败\n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}//将共享内存段映射到调用进程的数据段中msg = (struct shared_msg *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);if (msg < (struct shared_msg *)0){fprintf(stderr, "共享内存段映射到进程失败n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}printf("共享内存地址 %X\n", (int*)msg);//向共享内存中写入数据while (1){//向共享内存中写入数据printf("请输入消息:");//从缓冲区输入fgets(buf, BUFSIZ, stdin);strncpy(msg->text, buf, BUFSIZ);msg->update = 1; // 1表示数据更新,客户端要同步更新printf("更新数据完成\n");//写入数据if (strncmp(buf, "EOF", 3) == 0){break;}}//将共享内存和当前进程分离if (shmdt(msg) < 0){fprintf(stderr, "将共享内存和当前进程分离失败\n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}printf("程序结束\n");exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
tes2
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include struct shared_msg
{int update; //更新数据标志,1:更新,0:未更新char text[BUFSIZ]; //记录写入和读取的文本
};
void main()
{printf("程序开始\n");key_t key; //共享内存键值int shmid; //共享内存标识struct shared_msg *msg; //共享内存地址char buf[BUFSIZ]; //读取缓冲//得到键值key = (key_t)1234;//创建共享内存shmid = shmget(key, sizeof(struct shared_msg), IPC_CREAT | 0666);if (shmid < 0){//输出到错误缓冲区fprintf(stderr, "创建共享内存失败\n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}//将共享内存段映射到调用进程的数据段中msg = (struct shared_msg *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);if (msg < (struct shared_msg *)0){fprintf(stderr, "共享内存段映射到进程失败n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}printf("共享内存地址 %X\n", (int*)msg);//向共享内存中写入数据while (1){//服务端更新数据则读取while (msg->update == 1){sprintf(buf, "%s", msg->text);printf("读取数据:%s", buf);//读取完成后,将更新标志改变msg->update = 0;}if (strncmp(buf, "EOF", 3) == 0){break;}}//将共享内存和当前进程分离if (shmdt(msg) < 0){fprintf(stderr, "将共享内存和当前进程分离失败\n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}//删除共享内存if (shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) == -1){fprintf(stderr, "删除共享内存失败\n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}printf("程序结束\n");exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}










上一篇:Spring中有哪些设计模式
下一篇:【校内篇】如何安装一台虚拟机
相关内容
热门资讯
喜欢穿一身黑的男生性格(喜欢穿...
今天百科达人给各位分享喜欢穿一身黑的男生性格的知识,其中也会对喜欢穿一身黑衣服的男人人好相处吗进行解...
网络用语zl是什么意思(zl是...
今天给各位分享网络用语zl是什么意思的知识,其中也会对zl是啥意思是什么网络用语进行解释,如果能碰巧...
发春是什么意思(思春和发春是什...
本篇文章极速百科给大家谈谈发春是什么意思,以及思春和发春是什么意思对应的知识点,希望对各位有所帮助,...
苏州离哪个飞机场近(苏州离哪个...
本篇文章极速百科小编给大家谈谈苏州离哪个飞机场近,以及苏州离哪个飞机场近点对应的知识点,希望对各位有...
为什么酷狗音乐自己唱的歌不能下...
本篇文章极速百科小编给大家谈谈为什么酷狗音乐自己唱的歌不能下载到本地?,以及为什么酷狗下载的歌曲不是...
家里可以做假山养金鱼吗(假山能...
今天百科达人给各位分享家里可以做假山养金鱼吗的知识,其中也会对假山能放鱼缸里吗进行解释,如果能碰巧解...
四分五裂是什么生肖什么动物(四...
本篇文章极速百科小编给大家谈谈四分五裂是什么生肖什么动物,以及四分五裂打一生肖是什么对应的知识点,希...
华为下载未安装的文件去哪找(华...
今天百科达人给各位分享华为下载未安装的文件去哪找的知识,其中也会对华为下载未安装的文件去哪找到进行解...
怎么往应用助手里添加应用(应用...
今天百科达人给各位分享怎么往应用助手里添加应用的知识,其中也会对应用助手怎么添加微信进行解释,如果能...
客厅放八骏马摆件可以吗(家里摆...
今天给各位分享客厅放八骏马摆件可以吗的知识,其中也会对家里摆八骏马摆件好吗进行解释,如果能碰巧解决你...