React源码解读之任务调度
React 设计体系如人类社会一般,拨动时间轮盘的那一刻,你便成了穿梭在轮片中的一粒细沙,角逐过程处处都需要亮出你的属性,你重要吗?你无可替代吗?你有特殊权限吗?没有,那不好意思,请继续在轮片中循环。属于你的生命之火殆尽,前来悼念之人很多,这幕,像极了出生时的场景。
干啥玩意儿,这是技术文章不是抒情散文!下面进入正题。
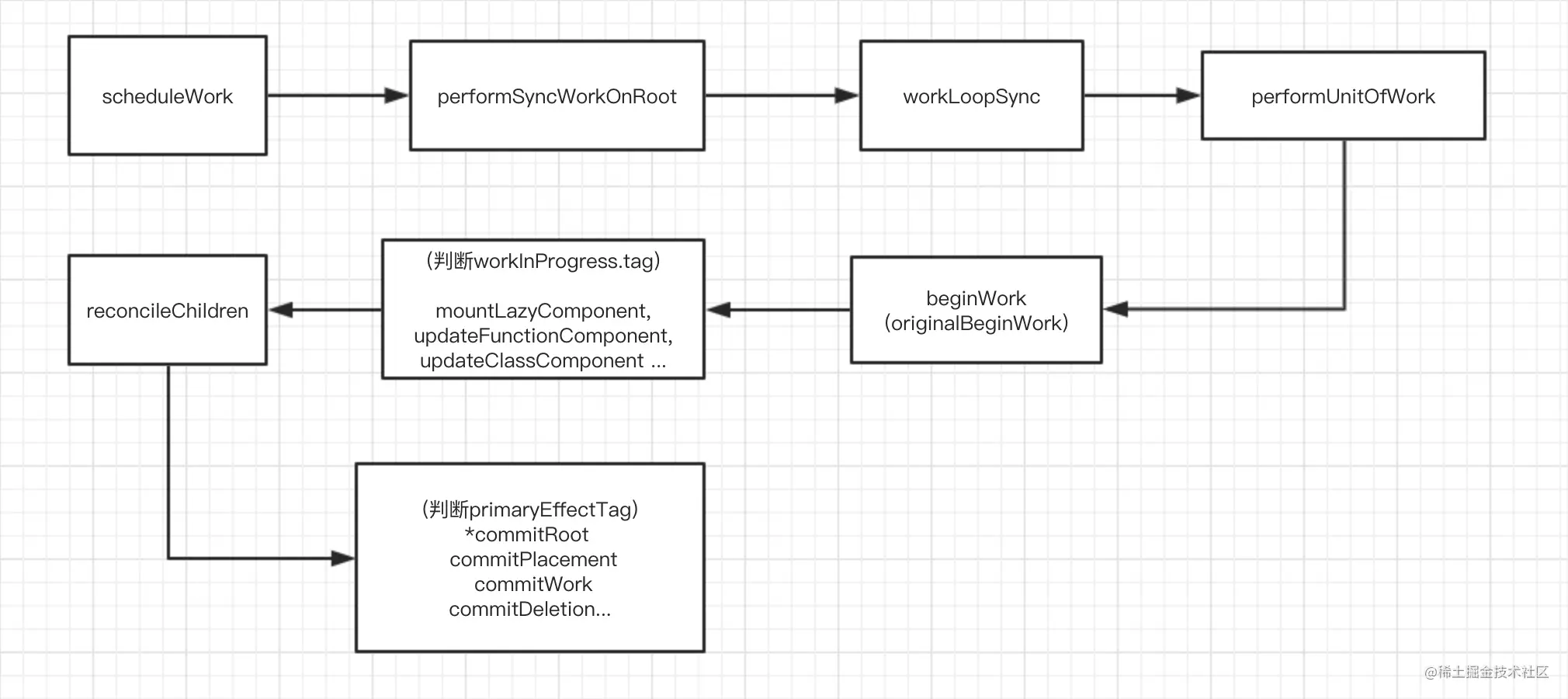
创建的准备上一节已经说明了,主要定义与更新相关的数据结构和变量,计算过期时间等。完成这些准备工作之后,正式进入调度工作,调度过程实现思路是:当与更新或挂载相关api被调用时,就会执行更新的逻辑,更新大致分为以下几个小阶段
scheduleWork
该步骤的主要工作有以下几点
- 通过
scheduleWorkOnParentPath方法找到当前Fiber的root节点 - 遍历当前更新节点父节点上的每个节点,对比每个节点的
expirationTime,如果大于当前节点,则将其值赋值为当前节点的expirationTime值。同时,childExpirationTime的值也是该的逻辑
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber: Fiber,expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
) {checkForNestedUpdates();warnAboutInvalidUpdatesOnClassComponentsInDEV(fiber);const root = markUpdateTimeFromFiberToRoot(fiber, expirationTime);if (root === null) {warnAboutUpdateOnUnmountedFiberInDEV(fiber);return;}checkForInterruption(fiber, expirationTime);recordScheduleUpdate();// TODO: computeExpirationForFiber also reads the priority. Pass the// priority as an argument to that function and this one.const priorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel();if (expirationTime === Sync) {if (// Check if we're inside unbatchedUpdates(executionContext & LegacyUnbatchedContext) !== NoContext &&// Check if we're not already rendering(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext) {// Register pending interactions on the root to avoid losing traced interaction data.schedulePendingInteractions(root, expirationTime);performSyncWorkOnRoot(root);} else {ensureRootIsScheduled(root);schedulePendingInteractions(root, expirationTime);if (executionContext === NoContext) {flushSyncCallbackQueue();}}} else {ensureRootIsScheduled(root);schedulePendingInteractions(root, expirationTime);}...
}
export const scheduleWork = scheduleUpdateOnFiber;
如果过期时间等于我们定义的Sync常量对应值,则进一步判断这次更新的状态,如果不是 batchUpdates 什么时候不是这个状态呢?我们前面认识过,比如reder时,判断完这个状态后还需要保证这次的更新渲染已准备好,则开始处理。不过处理之前,还要进行一个操作就是pending interaction,与我们动作相关的内容数据需要保存于 pendingInteractionMap 中。相关参考视频讲解:进入学习
function scheduleInteractions(root, expirationTime, interactions) {if (!enableSchedulerTracing) {return;}if (interactions.size > 0) {const pendingInteractionMap = root.pendingInteractionMap;const pendingInteractions = pendingInteractionMap.get(expirationTime);if (pendingInteractions != null) {interactions.forEach(interaction => {if (!pendingInteractions.has(interaction)) {// Update the pending async work count for previously unscheduled interaction.interaction.__count++;}pendingInteractions.add(interaction);});} else {pendingInteractionMap.set(expirationTime, new Set(interactions));// Update the pending async work count for the current interactions.interactions.forEach(interaction => {interaction.__count++;});}const subscriber = __subscriberRef.current;if (subscriber !== null) {const threadID = computeThreadID(root, expirationTime);subscriber.onWorkScheduled(interactions, threadID);}}
}
经过以上处理,就能进入 performSyncWorkOnRoot 处理了
function performSyncWorkOnRoot(root) {// Check if there's expired work on this root. Otherwise, render at Sync.const lastExpiredTime = root.lastExpiredTime;const expirationTime = lastExpiredTime !== NoWork ? lastExpiredTime : Sync;if (root.finishedExpirationTime === expirationTime) {commitRoot(root);}...
}
好了,到这里一个expirationTime 为 Sync 的且不是unbatchedUpdates,的调度就完成了,我们发现这条流水线的操作还是容易理解的,好,我们现在进入另一个分支,就是 batchedUpdates
ensureRootIsScheduled(root);
schedulePendingInteractions(root, expirationTime);
if (executionContext === NoContext) {// Flush the synchronous work now, unless we're already working or inside// a batch. This is intentionally inside scheduleUpdateOnFiber instead of// scheduleCallbackForFiber to preserve the ability to schedule a callback// without immediately flushing it. We only do this for user-initiated// updates, to preserve historical behavior of legacy mode.flushSyncCallbackQueue();
}
首先需要确保一点,Root是否已经处理过调度相关工作,通过 ensureRootIsScheduled 方法为root创建调度任务,且一个root只有一个task,假如某个root已经存在了任务,换言之已经调度过,那么我们需要重新为这个task计算一些值。而后同样有一个 schedulePendingInteractions ,用来处理交互引起的更新,方式与上面提到的 pending interaction 类似。
另外,如果executionContext 为NoContext ,则需要刷新用于处理同步更新的回调队列 flushSyncCallbackQueue ,该方法定义在 SchedulerWithReactIntegration.js 中。
如此,周而复始,完成更新的调度过程,最终调用 performSyncWorkOnRoot ,进入下一阶段,
performSyncWorkOnRoot
同样的选择题,当前是否能直接去提交更新,yes or no ?
if (root.finishedExpirationTime === expirationTime) {// There's already a pending commit at this expiration time.// TODO: This is poorly factored. This case only exists for the// batch.commit() API.commitRoot(root);
}
这种情况是很少的,一般会进入这个判断的else,也就是
...
workLoopSync();
...function workLoopSync() {// Already timed out, so perform work without checking if we need to yield.while (workInProgress !== null) {workInProgress = performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);}
}
又开始了遍历,这个遍历中同样有我们上节分析过一些技巧,比如unitOfWork.alternate 用于节点属性的对比与暂存
function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): Fiber | null {// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate. Ideally// nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here means that we don't// need an additional field on the work in progress.const current = unitOfWork.alternate;startWorkTimer(unitOfWork);setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(unitOfWork);let next;if (enableProfilerTimer && (unitOfWork.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode) {startProfilerTimer(unitOfWork);next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, renderExpirationTime);stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(unitOfWork, true);} else {next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, renderExpirationTime);}resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV();unitOfWork.memoizedProps = unitOfWork.pendingProps;if (next === null) {// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.next = completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);}ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;return next;
}
可以看到执行完相关操作后,随着 beginWork 函数的调用正式进入更新阶段。
beginWork
该部分主要的工作就是更新,更新什么呢?我们第一节讲到 React 不同的组件使用?typeof 指定,针对这些不同类型的组件,定义了各自的处理方法,我们以常用的 ClassComponent 为例。
function beginWork(current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {const updateExpirationTime = workInProgress.expirationTime;...
而后首先判断当前的更新节点是否为空,若不为空,则执行相关逻辑
...
if (current !== null) {const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;if (oldProps !== newProps ||hasLegacyContextChanged() ||// Force a re-render if the implementation changed due to hot reload:(__DEV__ ? workInProgress.type !== current.type : false)) {// If props or context changed, mark the fiber as having performed work.// This may be unset if the props are determined to be equal later (memo).didReceiveUpdate = true;} else if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {didReceiveUpdate = false;...
此刻略知一二,前后props是否发生更改?根据不同的条件判断为 didReceiveUpdate 赋值。而后根据当前 workInProgress 的tag值判断当前的节点对应组件类型是什么,根据不同类型,进入不同方法进行处理。
switch (workInProgress.tag) {...
}
而后,同样根据该tag,执行更新组件逻辑
case ClassComponent: {const Component = workInProgress.type;const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;const resolvedProps =workInProgress.elementType === Component? unresolvedProps: resolveDefaultProps(Component, unresolvedProps);return updateClassComponent(current,workInProgress,Component,resolvedProps,renderExpirationTime,);
}
reconcileChildren
更新组件过程中,如果还有子节点,需要调度并更新
export function reconcileChildren(current: Fiber | null,workInProgress: Fiber,nextChildren: any,renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
) {if (current === null) {// If this is a fresh new component that hasn't been rendered yet, we// won't update its child set by applying minimal side-effects. Instead,// we will add them all to the child before it gets rendered. That means// we can optimize this reconciliation pass by not tracking side-effects.workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(workInProgress,null,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime,);} else {// If the current child is the same as the work in progress, it means that// we haven't yet started any work on these children. Therefore, we use// the clone algorithm to create a copy of all the current children.// If we had any progressed work already, that is invalid at this point so// let's throw it out.workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(workInProgress,current.child,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime,);}
}
其子节点的 Fiber 调度定义在 ReactChildFiber.js 中,这里不展开了。
commitRoot
轮回中完成以上调度过程,也该到了提交更新的时候了,该方法我们在刚开始就讲到了,那时略过,现在拾起。
function commitRoot(root) {const renderPriorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel();runWithPriority(ImmediatePriority,commitRootImpl.bind(null, root, renderPriorityLevel),);return null;
}
具体的实现在 commitRootImpl 方法中,该方法调用 prepareForCommit 为更新做准备,最终根据更新的类型不同使用不同策略进行更新
let primaryEffectTag =effectTag & (Placement | Update | Deletion | Hydrating);
switch (primaryEffectTag) {case Placement: {commitPlacement(nextEffect);// Clear the "placement" from effect tag so that we know that this is// inserted, before any life-cycles like componentDidMount gets called.// TODO: findDOMNode doesn't rely on this any more but isMounted does// and isMounted is deprecated anyway so we should be able to kill this.nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement;break;}case PlacementAndUpdate: {// PlacementcommitPlacement(nextEffect);// Clear the "placement" from effect tag so that we know that this is// inserted, before any life-cycles like componentDidMount gets called.nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement;// Updateconst current = nextEffect.alternate;commitWork(current, nextEffect);break;}case Hydrating: {nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Hydrating;break;}case HydratingAndUpdate: {nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Hydrating;// Updateconst current = nextEffect.alternate;commitWork(current, nextEffect);break;}case Update: {const current = nextEffect.alternate;commitWork(current, nextEffect);break;}case Deletion: {commitDeletion(root, nextEffect, renderPriorityLevel);break;}
}
提交更新相关的处理定义于 ReactFiberCommitWork.js 同样也要借助 tag,做不同策略的处理。
至此完成了任务调度的所有工作,当然在后面的过程,事件相关的处理是只字未提,React最新源码对于事件系统做了很大改动,我们放在后面章节详细讲解。React 源码设计之精妙无法言尽,并且只是略读,完成本系列的粗略讲解后,后续会有更深入源码讲解。读源码为了什么?
- 理解我们每天使用的框架工作原理
- 学习作者NB的设计和对于代码极致的追求,运用到自己的项目中